Relational databases
Relational databases are databases based on the relational model.
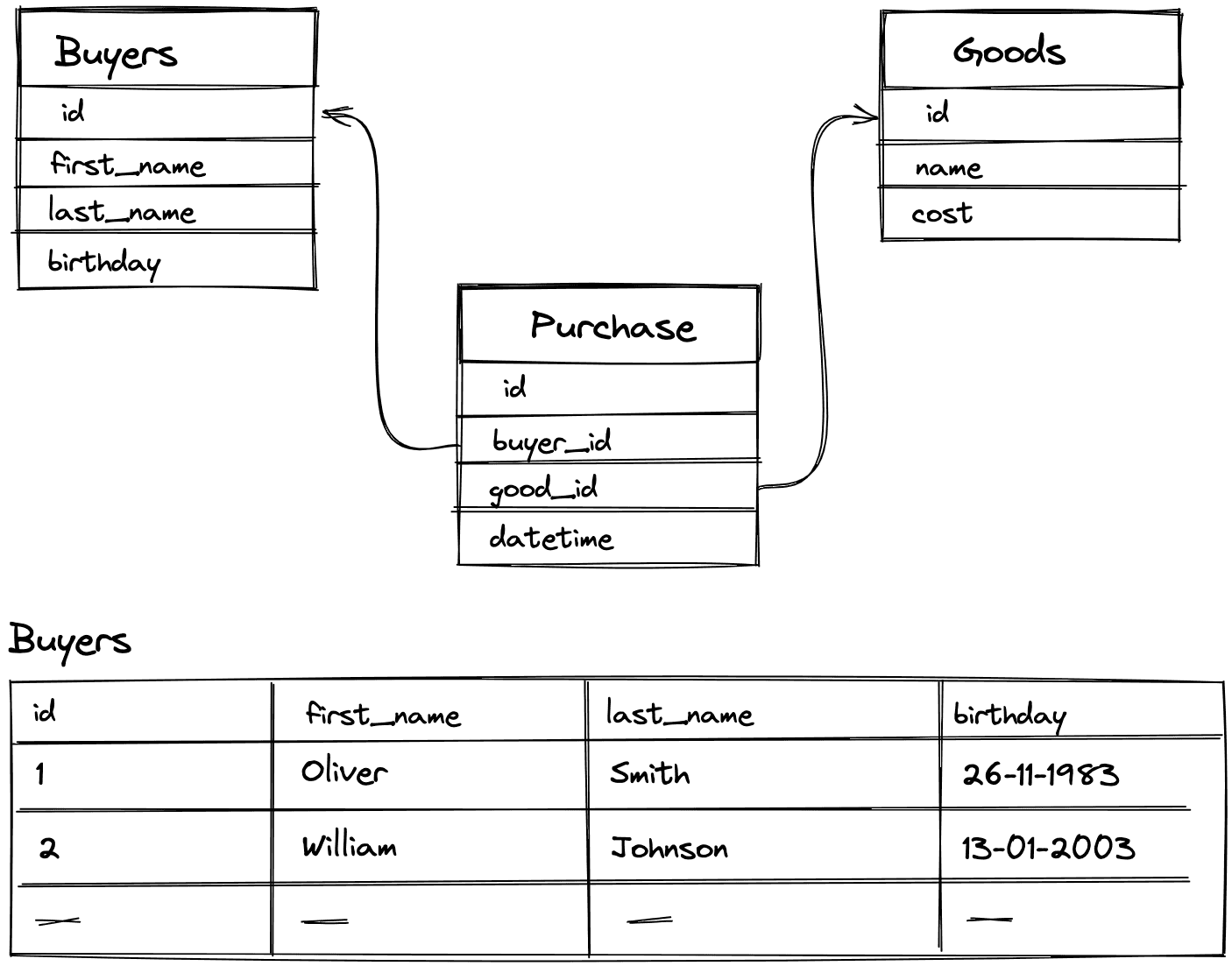
Data in relational structures is organized as a set of tables, called relationships, consisting of columns and rows. Each row of the table is a set of related values related to a single object or entity. Each row in a table can be labeled with a unique identifier called a primary key, and rows from multiple tables can be linked using foreign keys.
Example of a relational database
Features of relational databases
- The data model in relational databases is defined in advance and is strictly typed
- Data is stored in tables consisting of columns and rows
- Only one value is allowed at the intersection of each column and row
- Each column is named and has a specific type, followed by values from all rows in this column
- The columns are arranged in a certain order, which is determined when creating the table
- There may not be a single row in the table, but there must be at least one column
- Queries to the database return the result in the form of tables
We will consider more detailed features and principles of relational databases in the future, since they are of particular interest to us when studying SQL.
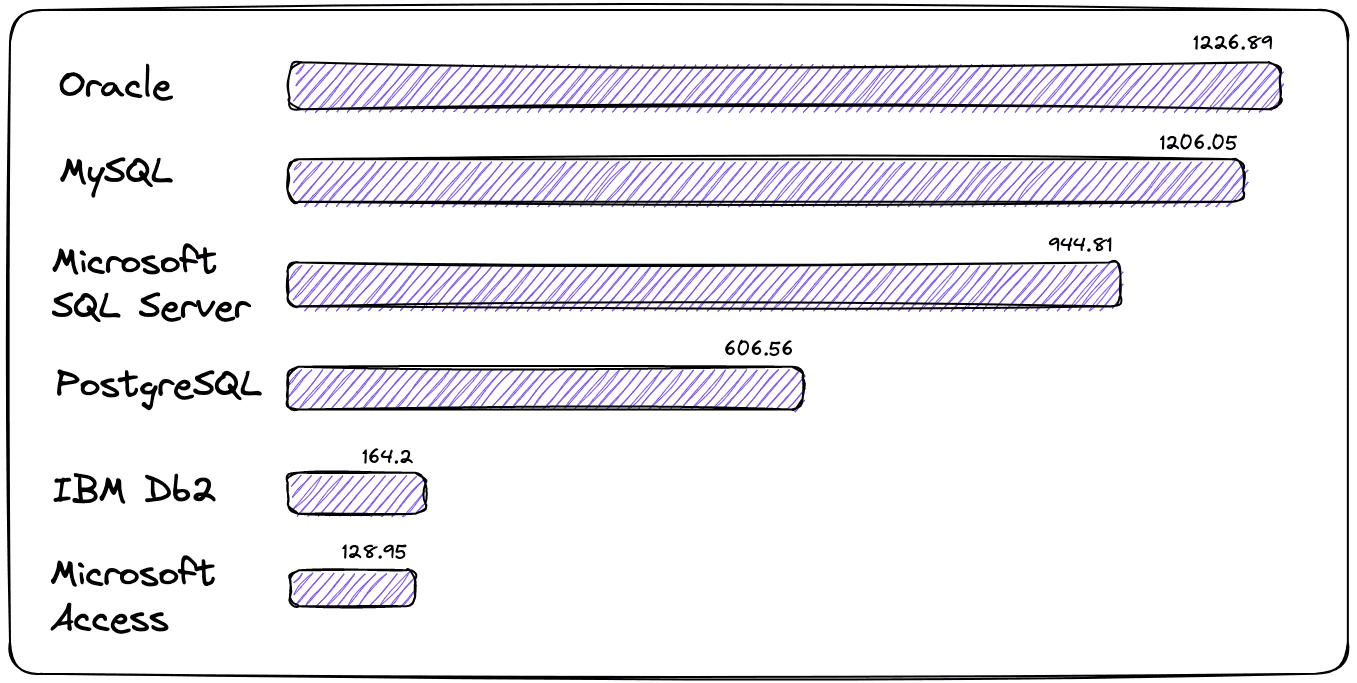
Ranking relational databases by popularity