Key-value databases
Key-value databases are a type of databases that store data as a collection of key–value pairs in which the key serves as a unique identifier.
That is, an unambiguous match of the value by key is created. Both keys and values can represent anything from simple to complex composite objects.
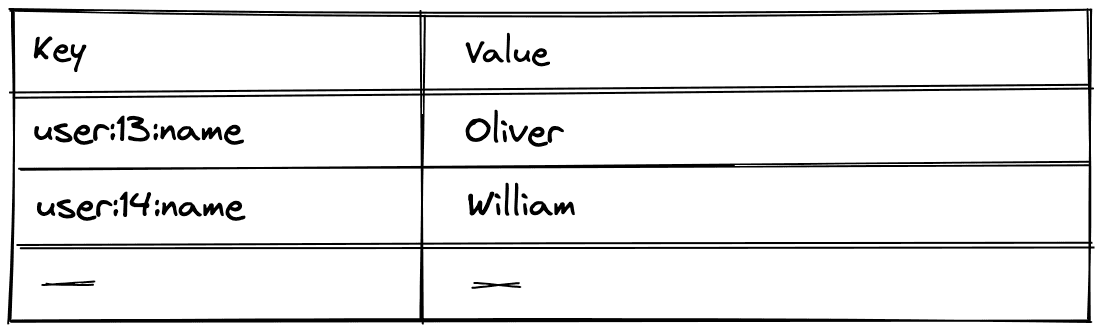
Example of a key-value database
Advantages
- Speed of operation
- Simplicity of the data storage model
- Flexibility: values can be any, including JSON
Disadvantages
- Poorly scaled as data models become more complex
- Inefficiency when working with a group of records
The standard implementation provides no insight into what the actual value contains—when you retrieve a value using its key, you have no guarantee of what you are getting. This means that you may have to filter or process data that you don't need in your application code. Typically, this will be less efficient in terms of performance compared to doing more of this work in the database.
- Lack of a query language
This means that the logic that is typically stored in the database is now in your application code, which can lead to complexity and complicate code maintenance.
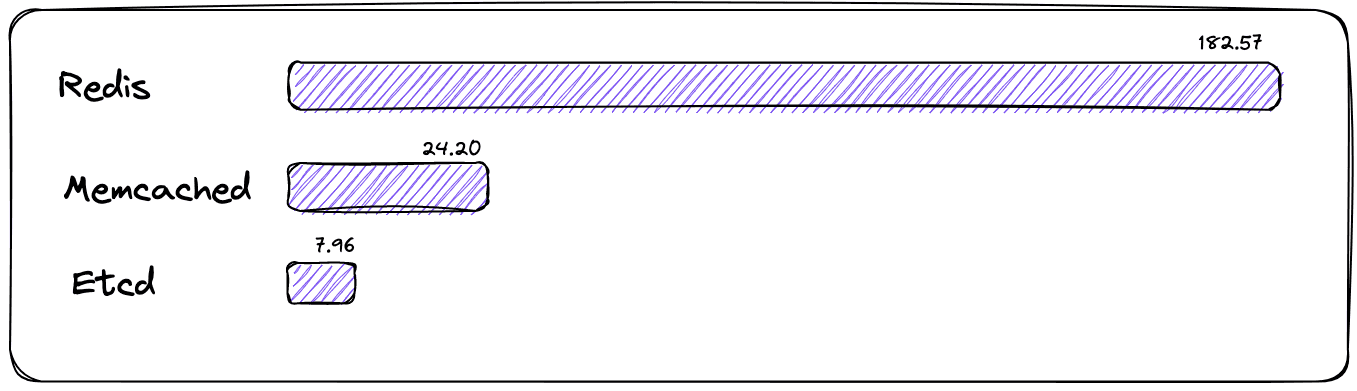
Ranking of Popular Key-value DBMS