Document-oriented databases
Document-oriented databases are a type of database designed to store and query data in the form of documents, similar to JSON.
Unlike other databases, document-oriented databases operate on "documents" grouped into collections. A document is a set of attributes (a key and its corresponding value). Values can be simple data types such as strings, numbers, or dates, as well as more complex types such as nested objects, arrays, and references to other documents.
Example of data storage


Features of document-oriented databases
In relational databases, the structure of records is strictly defined, and each record contains the same fields. Even if a field is not used, it is present, albeit empty.
Document-oriented databases, on the other hand, use a different approach: they do not have a data schema, allowing new information to be added to certain records without requiring all other records in the database to have the same structure.
Documents in the database are addressed using a unique key, usually a string that is automatically generated. This key can be used, for example, to retrieve a record or to reference other documents.
Another significant feature of document-oriented databases is that, in addition to simple searching for documents by key, as in key-value databases, they provide their own query language, functionality, syntax, and performance, which can vary from one implementation to another.
For example, this is what a query might look like in the most popular representative of this type of database - MongoDB:
> db.users.find({"name": "Daniel"}).count() > 1
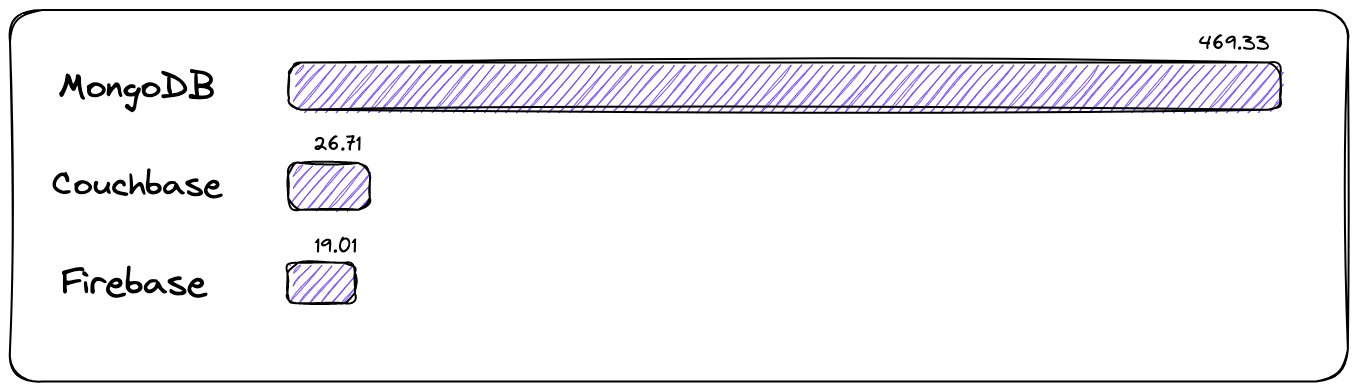
Rating of DBMS by popularity