Fundamental window functions
In previous articles, we have examined how window functions work and introduced the concept of a data window, which is passed to the window function. Now it's time to look at the types of window functions available.
Types of window functions
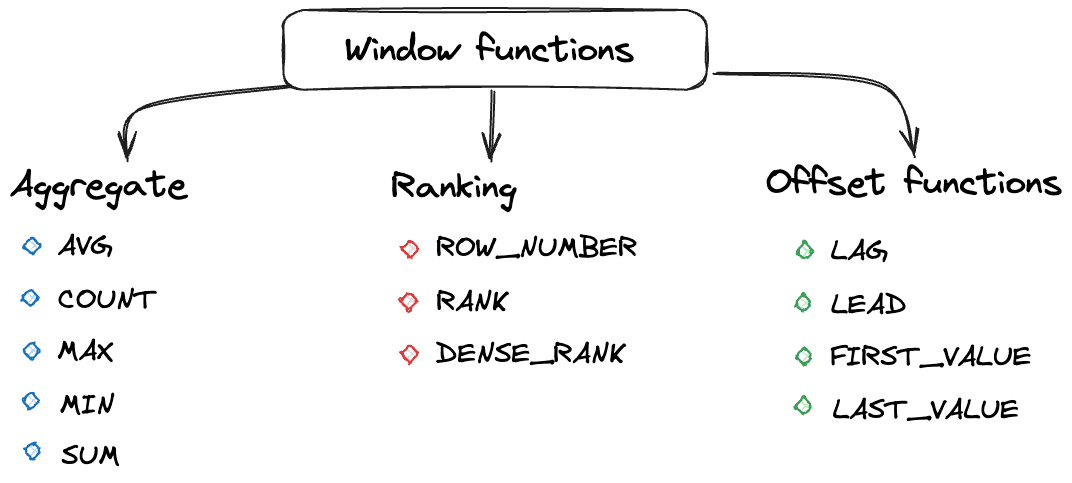
Window functions can be divided into 3 groups:
- Aggregate window functions
- Ranking window functions
- Offset window functions
Aggregate window functions
Aggregate functions are those that perform arithmetic calculations on a data set and return a total value.
- SUM — calculates the total sum of values;
- COUNT — counts the total number of records in a column (NULL values are not counted);
- AVG — calculates the arithmetic mean;
- MAX — finds the highest value;
- MIN — determines the lowest value.
MySQL 8.1SELECT id, home_type, price, SUM(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type) AS "Sum", COUNT(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type) AS "Count", AVG(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type) AS "Avg", MAX(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type) AS "Max", MIN(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type) AS "Min" FROM Rooms;
Ranking window functions
Ranking window functions are those that rank a value for each row in the window.
In ranking functions, the OVER keyword is followed by the mandatory ORDER BY condition, which determines the sorting order for ranking.
- ROW_NUMBER - returns the row number, used for numbering;
- RANK - returns the rank of each row. Here's how it works:
- Sorting: firstly, rows are sorted by one or more columns. These columns are specified in ORDER BY in the OVER clause.
- Assigning ranks: each unique row or group of rows that have the same values in the sorting columns is assigned a rank. The rank starts from 1.
- Identical values: if several rows have the same values in the sorting columns, they receive the same rank. For example, if two rows are in second place, both receive rank 2.
- Skipping ranks: after a group of rows with the same rank, the next rank increases by the number of rows in that group. For example, if two rows have rank 2, the next row will get rank 4, not 3.
- Continuing sorting: this process continues until ranks have been assigned to all rows in the result set.
- DENSE_RANK - returns the rank of each row. Unlike the RANK function, it doesn't skip ranks and after a group of identical values, the rank increases by one, not by the number of rows. For example, if two rows have rank 2, the next row will get rank 3, not 4.
MySQL 8.1SELECT id, home_type, price, ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "row_number", RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "rank", DENSE_RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "dense_rank" FROM Rooms;
Offset window functions
Offset window functions are those that allow moving and accessing different rows in the window relative to the current row, as well as accessing values at the beginning or end of the window.
-
LAG - accesses data from previous rows of the window.
It has three arguments: the column whose value needs to be returned, the number of rows to offset (default is 1), and the value to return if the offset returns a NULL value.
-
LEAD - accesses data from following rows. Similar to LAG, it has 3 arguments.
-
FIRST_VALUE - returns the first value in the window. Takes a column as an argument, the value of which needs to be returned.
-
LAST_VALUE - returns the last value in the window. Takes a column as an argument, the value of which needs to be returned.
MySQL 8.1SELECT id, home_type, price, LAG(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "lag", LAG(price, 2) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "lag_2", LEAD(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "lead", FIRST_VALUE(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "first_value", LAST_VALUE(price) OVER(PARTITION BY home_type ORDER BY price) AS "last_value" FROM Rooms;