INNER JOIN
In the previous lesson, we looked at the general structure of a multi-table query:
MySQL 8.1SELECT table_fields FROM table_1 [INNER] | [[LEFT | RIGHT | FULL][OUTER]] JOIN table_2 ON join_condition [[INNER] | [[LEFT | RIGHT | FULL][OUTER]] JOIN table_n ON join_condition]
When it comes to a multi-table query with an inner join, the general structure looks like this:
MySQL 8.1SELECT table_fields FROM table_1 [INNER] JOIN table_2 ON join_condition [[INNER] JOIN table_n ON join_condition]
For example, a query might look like this:
MySQL 8.1SELECT family_member, member_name FROM Payments INNER JOIN FamilyMembers ON Payments.family_member = FamilyMembers.member_id
Since JOIN is executed as an INNER JOIN by default if no parameters are specified, INNER is optional for an inner join.
Concept of inner join
An inner join is a type of join that returns only the rows that have matching values in both tables based on the join condition. It creates a new table that includes fields from both the first and second tables.
Visually, this looks like:
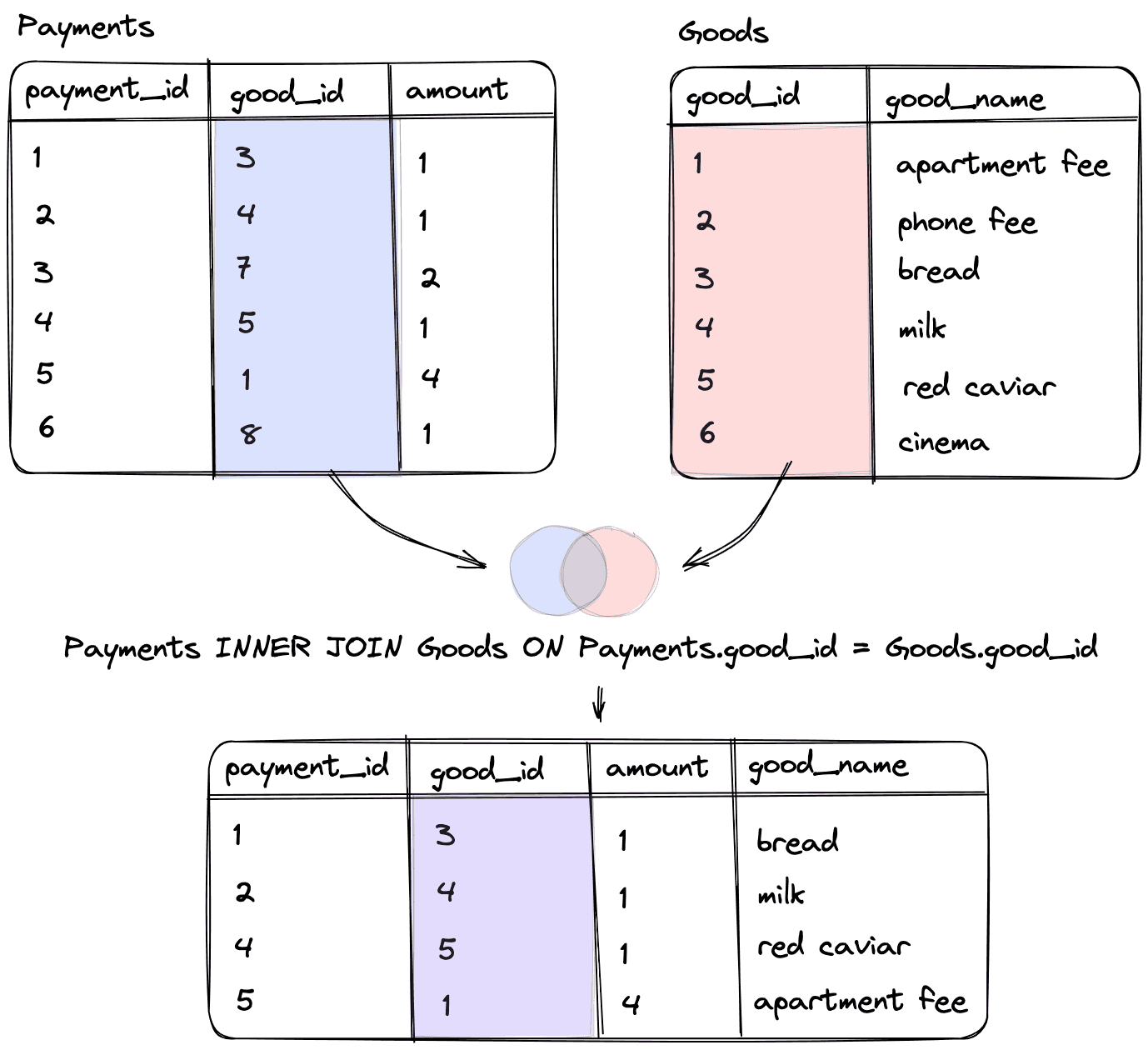
Since our condition specifies that Payments.good_id is equal to Goods.good_id, only the records where both tables have the same good_id value will be included in the resulting query.
Using WHERE to join tables
You can also use the WHERE operator to join tables internally. For example, the above query, written using INNER JOIN, will look like this:
MySQL 8.1SELECT family_member, member_name FROM Payments, FamilyMembers WHERE Payments.family_member = FamilyMembers.member_id